Overview
Medically reviewed by Dr. Rabeya Afroz Shomi
What is Measles?
Measles may be a highly communicable illness caused by morbillivirus. This virus replicates within the nose or pharynx of an infected child or adult. If an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks, the droplets spread within the air and people may inhale them. The infected droplets can also drop onto surfaces where they continue to be active and contagious for hours. People get infected by touching these surfaces then putting the infected fingers in their mouth, nose or rubbing their eyes following contact with the surfaces. Anyone who hasn’t been immunised or hasn’t had the infection within the past can get the infection. it's found that the infection clears in around seven to 10 days. Once you've got had measles, your body develops resistance then you don’t really get re-infected. But, it's going to sometimes cause serious complications like encephalitis and pneumonia.
What are the symptoms of measles?
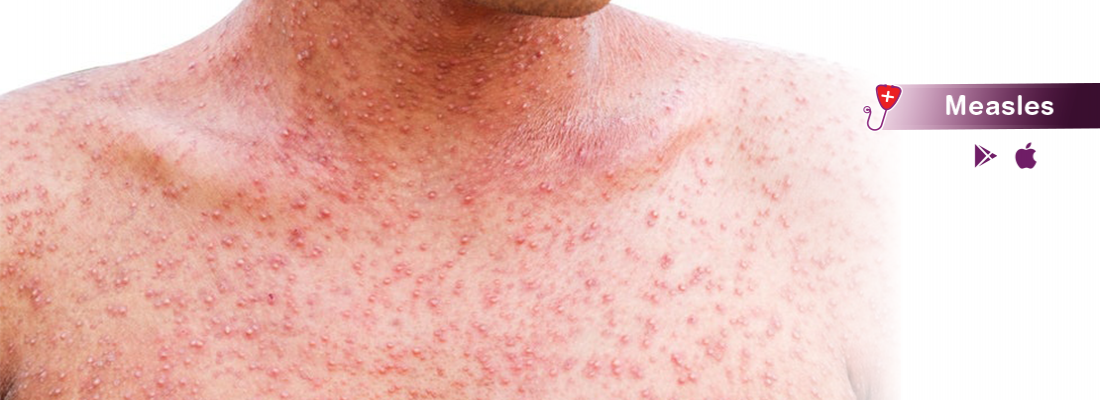
Measles starts with cold-like symptoms that starts around 10 days after getting infected. this is often followed by a rash few "> a few couple of days later. within the majority of patients, the ailment lasts for about seven to nine days. The initial Symptoms are: Runny or blocked nose Sneezing Watery eyes Puffy eyelids Red and sore eyes that are sensitive to light High grade fever Small greyish-white spots within the mouth Aches and pains Loss of appetite Tiredness, irritability and generalised malaise After few days you'll also experience the subsequent symptoms: Spots within the mouth: Some people develop small greyish-white spots within the mouth each day or two before developing the standard rash. Not everyone gets these spots but if they are doing develop additionally to other symptoms, they're more diagnostic of the infection. These spots may last for a few of days before disappearing. Measles rash: These rashes appear in 2 to three days after the infection and get away during a week. Measles Rash occurs as flat red-brown spots which may join together to make larger blotchy patches. It generally appears on the top and neck before spreading bent the remainder of the body. Itching could also be felt by some people. Rash is rare if the person has been immunised. Rashes that appear in measles look almost like roseola or rubella and slapped cheek syndrome.
What is the mode of transmission for measles?
Measles is very contagious and spreads through coughing or sneezing. this is often because the virus lives within the mucosae of nose and throat. The virus lives for about 2 hours within the atmosphere where an infected patient has sneezed or coughed. If anyone else inhale the contaminated air or touch the infected surface, then they will also get infected from the virus. Measles is contagious and 90% of the people that are on the brink of an infected individual and not resistant to the virus can get infected. Measles may be a human infection and isn't spread by any animal species.
How is measles spread?
Measles may be a highly contagious illness and is caused by morbillivirus. The virus replicates within the nose or pharynx of the patient and spreads through coughing or sneezing by an infected person. This disease occurs among poorly nourished children and adults who have a nutritional deficiency of vitamin A . Women infected with measles while pregnant can also develop complications and should end in stillbirth or miscarriage or maybe preterm birth. people that develop measles once are usually immune for the remainder of their lives.
What is the time period for measles?
Around 90% of susceptible individuals who are available contact with someone with the virus, develop the infection. The virus remains active on a surface for about 2 hours where an infected patient has sneezed or coughed. Measles remain active for a minimum of 4 days before the standard rash appears and stay contagious for subsequent few days. When the virus enters the system, replication of virus takes place within the lungs, throat and systema lymphaticum . The virus also multiplies within the eyes, central systema nervosum , tract and blood vessels. The virus stays for about 1 to three weeks within the system after the initial infection. Causes and Risk factors The measles virus is in a position to measure on the surface for several hours, causing the infected particles to stay within the air and intrinsically a person within its vicinity may get infected. Sharing utensils like spoons, towels, brush etc. with an infected person increases the danger of infection. Studies showed that measles was the first cause for death among children worldwide. the planet Health Organization (WHO) reported that the majority of the victims in its reports were children under the age of 5. The disease is found to mostly occur in unvaccinated children. Some parents have a wrong notion that vaccination can cause certain side effects in their children. it's not entirely true. Only within the rarest of cases the vaccine has been found to cause deafness, brain damage, coma, deafness and autistic characteristics. Children who lack vitamin A in their diet are at an increased risk of measles. Diagnosing and Treating Measles An experienced doctor would be ready to tell the case by examining rashes on your skin and checking for characteristic symptoms of the disease like whitish spots in and round the mouth, cough and pharyngitis . A biopsy could also be conducted for further affirmation. As such, there's no prescription medication to treat measles. The symptoms of the virus appear within two or three weeks. The doctor may prescribe medications and supplements to ease the symptoms and help your system .
What are the side effects of measles?
Common Side Effects: diarrhea and vomiting resulting in dehydration conjunctivitis middle ear infection (otitis media) which may cause earache laryngitis bronchitis, croup and pneumonia febrile seizures(fits caused by fever) Uncommon Side Effects: Hepatitis squint if the virus affects the muscles and nerves of the eyes meningitis and encephalitis Rare Side Effects: optic neuritis(infection of the optic nerve) resulting in vision loss heart and systema nervosum problems subacute sclerosing panencephalitis(SSPE),a fatal brain complication which occurs years after the measles infection(occurs in 1 in 25,000 cases) Measles in pregnancy: If you're not previously exposed or immunised and obtain pregnant, there's a risk of: miscarriage or stillbirth premature delivery low birth weight Measles in children: a toddler with measles can develop a bacterial infection and should have the subsequent symptoms: shortness of breath sharp pain which can worsen with every breath coughing up blood drowsiness confusion convulsions Complications surrounding Measles Severe complications: Some people suffer from severe complications like pneumonia & encephalitis and that they may even die due to these complications. Out of those , pneumonia has been the causative factor for death in about 1 out of each 20 children. Also, measles causes encephalitis in about 1 out of 100 patients which further cause convulsions, deaf ear and intellectual disability. Long term complications: Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) may be a rare ailment of the central systema nervosum which will occur thanks to measles infection of the brain. It occurs about 7 years after measles infected the person. Approximately five to 10 cases per million are reported for Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis.
What sort of precautions for measles?
These are the precautions for measles that has got to be exercised: 1.Vaccine: Measles infection are often prevented by taking the MMR vaccine (Measles, Mumps, Rubella). If the MMR vaccine isn't appropriate, human normal immunoglobulin(HNIG) are often used. Routine Vaccine-One dose is given when the kid is 12 to 13 months old. A second dose is given when the kid is 3 years old. Both adults and youngsters are often vaccinated at anytime if they need not been fully vaccinated before. If you're unsure whether you've got been vaccinated or not before, getting immunised again will do no harm. A dose of the MMR vaccine also can tend to anyone over the age of 6 months if they're in danger of getting infected as in: Case of outbreak of measles in your local area Close contact with an infected individual Travelling to a neighborhood where the infection is widespread. 2. HUMAN NORMAL IMMUNOGLOBULIN(HNIG) This is basically a mix of antibodies that have the power to offer short-term but immediate protection from measles. it's recommended to: Babies but 6 months aged . Pregnant women who are either not immunised or not exposed to the virus. Susceptible individuals like those with HIV or Leukemia. 3. Stop the spread of the virus: This can be achieved by doing the following: Stop attending school or work if you're exposed to the virus Avoid getting into contact with patients who have this infection
